Conference Information
Welcome Message


Welcome Message:
Wind and Renewable Energy Conferences 2023 welcomes all the experts and delegates down the globe to meet and network with different and multiple renowned people to the most happening event of Wind & Renewable Energy Conferences 2023 under the theme of "Harvesting the Power of Nature : Advancements in Wind and Renewable Energy"
Hybrid Event: You can participate In-person at Berlin, Germany or join Online/Virtually from your home or work.
Wind & Renewable Energy Conferences 2023 welcomes you to join us on the most happening event on 11-13 of September, 2023. We cordially invite all experts from academia, business, and industry to contribute to and shape this Wind and Renewable Energy conference 2023 by submitting research abstracts, papers, and posters from around the world. Finally, the Wind and Renewable Energy Conferences promotes global interdisciplinary collaboration and exchange among technologists. This website gives you access to all the information and materials needed for your conference event. You can quickly find information about registration, accommodation, travel, venues, speakers and much more.
Germany might be a fantastic venue for the attendees of conference to enjoy and nurture all the attractions and amusements of Germany.
Germany is looking forward to greet you!!!
With Regards
Program Manager
Wind Energy Conference!!!
About us
Mark your calendars for the most enthusiastic conferences held around the year “ WIND AND RENEWABLE ENERGY” conference. Wind Energy conferences team gaily announce Wind and Renewable energy conferences to be held on September 11-13 @ Berlin, Germany under the theme of "Harvesting the Power of Nature : Advancements in Wind and Renewable Energy".
One of the most prominent forms of renewable energy is wind energy, which has become significantly popular in recent years. Wind energy is a kind of renewable energy obtained from the kinetic energy of the wind. It is clean, sustainable and has abundant source of energy which has a wide spread in recent years.
This is done using Wind turbines, a large structure consisting of a tower, rotor blades, a generator, and a control system. The amount of energy that a wind turbine produces depends on several factors including wind speed, rotor blade size and design and generator efficiency. Wind turbines are designed to operate in a specific range of wind speed typically 3 to 25 meters per second. If the wind speed is too low the turbine cannot produce enough power to be economically viable, but if the wind speed is too high, the turbine may shut down to avoid damage.
Let's know the different forms of renewable energy that commonly accompany wind power.
Solar energy
Hydropower
Geothermal energy
Biomass energy
WHY TO ATTEND?
- For those with an interest in the industry, attending a wind energy conferences can have a lot of advantages.
- Attendees can access leading authorities, important figures, cutting-edge research, and industry specialists by attending wind energy conferences.
- Also, by networking with other professionals, they may share information and views and learn about the most recent developments in wind energy.
- Attending wind energy conference can also help people stay current on changes to laws and policies and spot possibilities for advancement.
- In conclusion, going to a wind energy conference can help people progress their careers in this dynamic and quickly changing industry by expanding their knowledge and expertise.
Market Analysis
The global wind energy market is expected to grow at a steady pace in the coming years, driven by increasing demand for wind energy and the declining cost of wind power generation. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global wind energy market was valued at USD 127.14 billion in 2020 and is projected to have an compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.4% from 2021 to 2028.
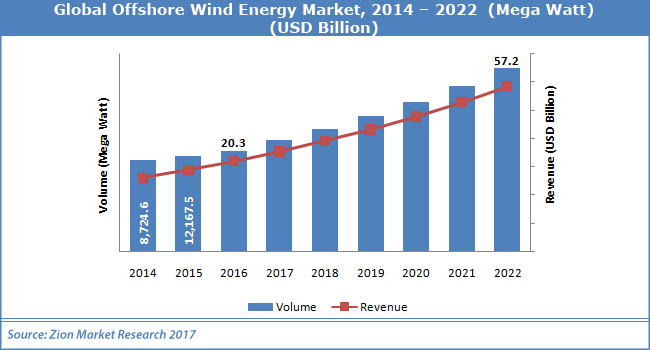
The onshore wind energy segment has accounted for the largest share of the global wind energy market in 2020, with a market size of USD 97.52 billion or 76.7% of the total market. The offshore wind energy segment is expected to grow at a faster pace, with a CAGR of 14.5% from 2021 to 2028, driven by the increasing number of offshore wind farms and the development of larger wind turbines.
Geographically, Asia Pacific is the largest wind energy market, accounting for 46.6% of the total market in 2020. China is the largest market in the region, with a market size of USD 57.22 billion in 2020, followed by India and Japan. Europe is the second-largest market, with a market size of USD 38.54 billion in 2020, followed by North America.
The wind energy market is highly competitive, with a large number of players operating in the market. Some of the key players in the market include Vestas Wind Systems A/S, Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, General Electric Company, Goldwind Science & Technology Co. Ltd., and Nordex SE.
The global wind energy showcase is anticipated to develop at a solid pace over the coming years, driven by expanding requests for renewable energy and favorable government arrangements. The coastal wind vitality fragment is anticipated to proceed to rule the advertise, whereas the seaward wind vitality fragment is anticipated to develop at a speedier pace. Asia Pacific is the biggest advertise for wind vitality, with China as the biggest showcase within the locale. In addition to the expansion of wind energy, other renewable energy sources such as solar, hydro, geothermal and biomass are expected to grow rapidly. The showcase for vitality capacity frameworks is additionally anticipated to develop quickly, as renewable vitality sources end up a bigger portion of the vitality blend and lattice integration gets to be more challenging.
The outlook for the wind and renewable energy market is positive, with increasing investment and government support, advances in technology, and growing demand for clean energy driving growth and innovation in the industry.
Metrics
Pulsus is organizing an international symposium that aims to bring together leading researchers in the field of wind energy to explore the latest developments in renewable energy. The conference will cover a wide range of topics related to wind energy, including turbine technology, wind farm design, energy storage, grid integration, and many others. The Wind Energy Conference 2023 will feature keynote speakers, oral presentations, poster sessions, and exhibitions, providing participants with the opportunity to learn about the latest research and engage in fruitful discussions. Attendees will gain valuable insights into the current state of wind energy and its potential to meet our future energy needs.
Sessions & Tracks
1.Wind Energy: Wind energy is a form of renewable energy source that harnesses the power of wind to generate electricity. Wind turbines are typically placed in locations with consistent and strong wind patterns, such as on hills, ridges, or in coastal areas. When the wind blows, it turns the blades of the turbine, which spins a rotor connected to a generator, producing electricity. Advancements in wind turbine technology have made wind energy increasingly cost-competitive with traditional fossil fuel sources of electricity. In addition, wind energy is a clean and sustainable source of power, as it does not produce any greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants during operation. One potential challenge with wind energy is its intermittent nature, as wind speeds can vary and be unpredictable. However, this challenge can be addressed through the integration of energy storage technologies, such as batteries or pumped hydro storage, to store excess electricity generated during times of high wind speeds for use when the wind speeds are lower. Overall, wind energy has significant potential as a source of renewable energy to help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change, while also promoting energy security and independence.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
2. Wind Power Technology: Wind power technology harnesses the natural energy of the wind to generate electricity. It is a renewable and sustainable energy source that has gained significant momentum in recent years as an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels. The basic principle behind wind power involves the conversion of wind energy into mechanical energy through the use of wind turbines. Wind turbines consist of blades mounted on a tall tower, which rotate when the wind blows. The rotating blades drive a generator, producing electricity. These turbines can vary in size and capacity, from small units used in remote locations to massive offshore installations. One of the main advantages of wind power is its eco-friendliness. It produces no greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to the reduction of carbon footprints and mitigating climate change. Wind power also promotes energy independence and reduces reliance on finite resources. However, wind power also faces challenges. Wind is intermittent, and power generation depends on wind speed and consistency. To address this, advances in technology have led to more efficient turbines and energy storage solutions. In conclusion, wind power technology holds immense promise as a clean and sustainable energy source, playing a crucial role in the transition towards a greener future. Continued research and innovation will further enhance its potential, making it an integral part of the global energy mix.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
3. Wind Turbines Instrumentation: Wind turbines instrumentation refers to the various sensors, devices, and systems employed to monitor and control the performance and safety of wind turbines. This critical aspect of wind power technology ensures the efficient operation, early detection of potential issues, and overall reliability of the turbines. Wind turbine instrumentation includes a wide array of sensors to measure parameters such as wind speed, direction, temperature, and pressure. Anemometers and wind vanes assess the wind's characteristics to optimize turbine positioning for maximum energy capture. Nacelle-mounted sensors monitor generator and gearbox temperatures, vibration levels, and oil condition to identify maintenance needs and prevent failures. Load sensors and strain gauges help monitor the structural integrity of turbine components, ensuring that they can withstand the dynamic loads induced by wind forces. Additionally, yaw position sensors, pitch angle sensors, and speed sensors help control the turbine's orientation and blade pitch for optimal power output and safety. Data from these instruments are collected and analysed in real-time, providing valuable insights for operators and maintenance teams. Advanced control systems adjust turbine operation based on the collected data, maximizing energy production while protecting the equipment from extreme conditions. In conclusion, wind turbines instrumentation is a crucial aspect of wind power technology, enabling efficient operation, condition monitoring, and improved reliability. As wind energy continues to play a pivotal role in sustainable energy generation, continuous advancements in instrumentation technology will further enhance the performance and longevity of wind turbines.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
4. Renewable &Sustainable energy: Renewable and sustainable energy sources are crucial components of the global effort to address climate change and ensure a sustainable future. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, renewable energy sources are naturally replenished and have a minimal environmental impact. Solar energy harnesses the power of sunlight through photovoltaic cells or solar thermal systems, providing clean electricity and heat. Wind power technology converts wind energy into electricity using wind turbines, making it a reliable and widely available source. Hydropower utilizes the kinetic energy of flowing water to generate electricity, while geothermal energy taps into the Earth's heat from beneath its surface. Biomass energy involves converting organic materials like wood, agricultural residues, or municipal waste into heat or electricity. Embracing renewable and sustainable energy not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also fosters energy independence, job creation, and technological innovation. Governments, businesses, and individuals play essential roles in advancing these technologies to create a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
5. Solar Power Technology: Solar power technology harnesses the energy of the sun to generate electricity and heat. It is one of the most promising and widely adopted forms of renewable energy. Solar photovoltaic (PV) cells, commonly mounted on rooftops or in solar farms, convert sunlight directly into electricity. These cells contain semiconductor materials that generate a flow of electrons when exposed to sunlight. Solar thermal technology, on the other hand, uses mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver, which then converts it into heat to generate electricity or provide hot water for residential and industrial use. Solar power offers numerous benefits, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting energy independence, and lowering electricity costs over the long term. It has experienced significant technological advancements and cost reductions, making it increasingly competitive with conventional energy sources. However, solar power's intermittent nature and dependence on weather conditions necessitate energy storage solutions for consistent supply. Continued research and investment in solar power technology are vital to maximizing its potential and accelerating the transition towards a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
6. Offshore wind energy: Offshore wind energy is a type of renewable energy that involves the installation of wind turbines in bodies of water, such as oceans, seas, or large lakes. Offshore wind energy has several advantages over onshore wind energy, including stronger and more consistent wind speeds, reduced visual and noise impacts, and increased potential for larger and more efficient turbines. Offshore wind energy is still a developing industry, but it has the potential to become a major source of renewable energy in the future. The world's largest offshore wind farms are currently located in Europe, with the United Kingdom, Denmark, and Germany leading in installed capacity. However, offshore wind energy is also being developed in other regions of the world, including Asia and North America. Offshore wind energy faces several challenges, such as the high upfront costs of installation and maintenance, potential impacts on marine wildlife and ecosystems, and the need for specialized vessels and equipment for installation and maintenance. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these challenges and advancing offshore wind energy technology. Overall, offshore wind energy has significant potential as a source of renewable energy to help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change, while also promoting energy security and independence.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation|Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency|Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences|Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences|Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
7. On-shore wind energy: On-shore wind energy is a type of renewable energy that involves the installation of wind turbines on land, typically in locations with consistent and strong wind patterns. Onshore wind energy has several advantages over other types of renewable energy sources, including its relatively low installation and maintenance costs, its scalability, and its ability to be integrated with existing power grid infrastructure. On-shore wind energy is a mature industry and has been a major source of renewable energy in many parts of the world for several decades. The largest onshore wind farms are currently located in China, the United States, and Germany, with many other countries also developing significant onshore wind energy capacity. One potential challenge with onshore wind energy is its visual and noise impacts, which can be a concern for nearby communities. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on reducing these impacts through advancements in wind turbine technology and sound insulation. Overall, onshore wind energy has significant potential as a source of renewable energy to help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change, while also promoting energy security and independence.
Related Associations:German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation|Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency|Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences|Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences|Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
8. Smart grid integration: Smart grid integration refers to the incorporation of advanced digital technologies into the electrical grid to improve its efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. This involves the integration of various technologies, such as sensors, communication networks, advanced analytics, and automation, to create a more intelligent and responsive power system. One of the primary goals of smart grid integration is to enable greater integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the grid. This requires the development of new technologies and strategies to manage the intermittent nature of these energy sources and ensure that they are integrated into the grid in a way that is reliable and efficient. Smart grid integration can also enable greater energy efficiency by providing real-time information on energy usage, enabling consumers to adjust their energy consumption in response to changes in energy prices or demand. This can help to reduce energy waste and lower overall energy consumption. Other benefits of smart grid integration include improved grid resilience, increased reliability, and improved response to power outages or emergencies. It can also provide greater visibility and control over the power system, enabling utilities to identify and address issues more quickly and efficiently. Overall, smart grid integration is an important step towards creating a more efficient, reliable, and sustainable power system that can support the transition to a low-carbon economy and help to address the challenges of climate change.
Related Associations:German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation|Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency|Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences|Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences|Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
9. Future of Wind Energy: Wind power is a small but rapidly growing part of electricity generation. It accounts for five per cent of global electricity generation and 8 per cent of US electricity generation. Globally, wind power exceeds 743 gigawatts, more than grid-connected solar power and about half that of hydropower. Almost three-quarters of these 651 gigawatts come from wind farms in five countries: China, the United States, Germany, India and Spain. America's wind power capacity has tripled over the past decade. The wind is currently the dominant source of renewable energy in the United States, with enough wind turbines to generate more than 100 million watts, or megawatts, of electricity, equivalent to the consumption of about 29 million average homes. The price of wind energy has collapsed. over the past decade. In the US, it is competitive with natural gas and solar. Wind energy and solar energy complement each other because the wind is often strongest when the sun warms the earth for some time. Warm air rises from the hottest areas, leaving a vacuum into which other air can penetrate, creating horizontal wind currents. We can use solar energy at the beginning of the day and wind energy in the evening and at night. Wind power has added value in places that are too cloudy or dark to produce strong solar power, especially at higher latitudes.
Related Associations:German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation|Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency|Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences|Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences|Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
10. Solar Energy: Solar energy is a renewable energy source that involves the conversion of sunlight into electricity. Solar power is generated through the use of photovoltaic (PV) cells, which are made up of semiconductor materials that convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. The DC electricity is then converted into alternating current (AC) electricity through the use of an inverter, which can be used to power homes, businesses, and other applications. Solar energy has several advantages over other types of energy sources, including its sustainability, low environmental impact, and scalability. It can be used to power a wide range of applications, from small electronic devices to large-scale power plants. Additionally, solar energy systems can be installed on rooftops or other unused spaces, making them accessible to a wide range of users. There are also several challenges associated with solar energy, such as its relatively high installation and maintenance costs, its intermittency (since solar power generation is dependent on sunlight), and the need for energy storage solutions to store excess energy generated during periods of peak sunlight. Despite these challenges, the use of solar energy is growing rapidly around the world, with significant investments being made in solar power generation technology and infrastructure. Many countries have set ambitious goals for expanding their use of solar energy, with the aim of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting energy independence. Overall, solar energy has significant potential as a source of clean, renewable energy to help mitigate climate change and promote sustainable development.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation|Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency|Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences|Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences|Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
11. Hydro Energy: Hydro energy, also known as hydropower, is a renewable energy source that harnesses the power of moving water to generate electricity. Hydroelectric power plants use the energy of falling water to turn turbines that generate electricity, which can be used to power homes, businesses, and other applications. Hydro energy has several advantages over other types of energy sources, including its sustainability, low environmental impact, and scalability. It is a reliable source of electricity, as long as there is a consistent supply of water. Hydro power plants can also be used for a wide range of applications, from small-scale micro-hydro systems to large-scale hydroelectric dams. However, there are also some challenges associated with hydro energy. Hydro power plants can have significant environmental impacts, such as altering river ecosystems and affecting fish populations. Additionally, the construction and maintenance of hydro power plants can be expensive. Despite these challenges, hydro energy is an important source of renewable energy, and many countries around the world are investing in hydropower infrastructure to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable development. In some cases, hydro energy can also be used to complement other renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, by providing a reliable source of electricity when those sources are not available. Overall, hydro energy has significant potential as a source of clean, renewable energy to help mitigate climate change and promote sustainable development, as long as environmental impacts are carefully managed.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences|Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences|Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
12.Geo Thermal Energy: Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source that involves the use of the Earth's internal heat to generate electricity. This energy is generated through the use of geothermal power plants, which extract heat from deep within the Earth's crust and use it to generate steam, which is then used to turn turbines and generate electricity. Geothermal energy has several advantages over other types of energy sources, including its sustainability, low environmental impact, and reliability. Unlike wind and solar power, which are intermittent sources of energy, geothermal energy can provide a consistent and reliable source of electricity as long as the heat source is maintained. Additionally, geothermal power plants produce very little greenhouse gas emissions or other pollutants, making them a clean source of energy. However, there are also some challenges associated with geothermal energy. The development of geothermal power plants requires significant investment in drilling and exploration, and the technology is not yet as widely available or cost-competitive as some other renewable energy sources. Additionally, some geothermal resources may be located in sensitive areas, such as national parks or protected lands, which can limit their development. Despite these challenges, the use of geothermal energy is growing around the world, with significant investments being made in geothermal power plants and research into new geothermal technologies. Many countries have set ambitious goals for expanding their use of geothermal energy, with the aim of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable development. Overall, geothermal energy has significant potential as a source of clean, renewable energy to help mitigate climate change and promote sustainable development, as long as the associated environmental impacts and development costs are carefully managed.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation|Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency|Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences|Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences|Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
13.Biomass Energy: Biomass energy is a renewable energy source that involves the use of organic materials, such as wood, agricultural waste, and municipal solid waste, to generate electricity, heat, or other forms of energy. Biomass can be burned directly to produce heat or electricity, or it can be converted into biofuels such as ethanol or biodiesel. Biomass energy has several advantages over other types of energy sources, including its sustainability, availability, and potential for carbon neutrality. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and non-renewable, biomass is a widely available resource that can be sustainably harvested and used to generate energy. Additionally, biomass energy has the potential to be carbon-neutral, since the carbon dioxide released during biomass combustion is offset by the carbon absorbed during plant growth. However, there are also some challenges associated with biomass energy. The production and transportation of biomass can have significant environmental impacts, such as deforestation or air pollution from burning crop residues. Additionally, the efficiency of biomass energy production can vary widely depending on the type of biomass and the technology used. Despite these challenges, the use of biomass energy is growing around the world, with significant investments being made in bioenergy infrastructure and research into new biomass technologies. Many countries have set ambitious goals for expanding their use of bioenergy, with the aim of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable development. Overall, biomass energy has significant potential as a source of clean, renewable energy to help mitigate climate change and promote sustainable development, as long as the associated environmental impacts are carefully managed and the technology is developed in a sustainable and efficient way.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences|Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences|Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
14.Tidal Energy: Tidal energy is a form of renewable energy that is generated by harnessing the power of ocean tides. The gravitational pull of the moon and the sun causes the ocean tides to rise and fall regularly, which can be used to generate electricity. There are two main types of tidal energy technology: tidal barrages and tidal turbines. Tidal barrages are structures built across a river estuary or bay that trap the incoming tide and then release it through turbines to generate electricity. Tidal turbines, on the other hand, are similar to wind turbines but are submerged underwater, where they are turned by the flowing tide to generate electricity. Tidal energy has several advantages over other forms of renewable energy, including its predictability, reliability, and high energy density. However, it also has some challenges, such as high upfront costs, potential environmental impacts on marine ecosystems, and limited availability of suitable tidal sites.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
15.Energy Storage: Energy storage is the process of capturing and storing energy for later use. With the increasing use of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, energy storage has become an important area of focus for ensuring the reliability and stability of energy supply. There are several different types of energy storage technologies, including batteries, pumped hydro storage, compressed air energy storage, and thermal storage. Each of these technologies has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice of technology depends on factors such as cost, efficiency, scalability, and the specific application. Energy storage systems can help to balance the variability and intermittency of renewable energy sources by providing a buffer between energy supply and demand. They can also help to improve the efficiency and flexibility of the electricity grid, reduce energy costs, and enhance the resilience and reliability of energy supply in the event of power outages or emergencies.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
16.Renewable Energy Policy and Regulation: Renewable energy policy and regulations aim to promote the use of renewable energy sources in order to minimise greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere. Renewable energy laws and regulations, via incentives, can assist countries in meeting their climate objectives by boosting access to clean, cheap, and dependable power. Governments have formed international agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, which aims to reduce global emissions by setting goals for reducing greenhouse gas emissions over time. Countries have established protocols at the international level, such as the Paris Agreement, which attempts to reduce global emissions by setting objectives for lowering greenhouse gas emissions over time. Countries are urged to establish specialised renewable policies, such as Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS), which require minimum amounts of output or consumption from renewables in order to minimise carbon dioxide emissions. Furthermore, international organisations such as the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) offer technical assistance in developing national plans for the deployment of sustainable energy technologies, as well as capacity building efforts related to policy formulation and implementation at both the national and regional levels. We can make progress towards our climate targets while offering clean air benefits now by stimulating investment in renewables and establishing a low-carbon economy.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
17.Wind energy Innovations: Wind energy innovations have played a pivotal role in revolutionizing the renewable energy landscape. Advancements in wind turbine design, materials, and control systems have significantly improved the efficiency, reliability, and environmental sustainability of wind power. One major innovation is the development of larger and more powerful wind turbines. High-capacity turbines can capture more energy from the wind, reducing the number of turbines needed for a given capacity and minimizing their environmental footprint. Additionally, floating offshore wind farms have emerged as a promising innovation, unlocking the potential of deeper waters for wind energy generation. Advanced materials, such as carbon composites and smart coatings, enhance turbine performance and durability while reducing maintenance costs. Furthermore, innovative blade designs, such as biomimicry-inspired shapes, optimize energy capture and reduce noise. Wind farm management systems now use data analytics, machine learning, and predictive maintenance to optimize turbine performance, detect faults early, and improve operational efficiency. These innovations continue to drive down the cost of wind energy and reinforce its position as a key player in the global shift toward sustainable and clean energy sources.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
18. Third Generation Wind Power:Third-generation wind power refers to the latest and most advanced developments in wind energy technology. It encompasses cutting-edge innovations aimed at maximizing the efficiency and scalability of wind turbines. One significant aspect of third-generation wind power is the use of advanced materials in turbine construction. Lightweight composites, smart materials, and 3D printing techniques are employed to create stronger and more aerodynamic turbine components, leading to increased energy capture and reduced maintenance needs. Moreover, third-generation wind power emphasizes the development of larger and more powerful turbines, capable of harnessing higher wind speeds and generating greater electricity output. These larger turbines are particularly well-suited for offshore wind farms, where stronger and more consistent winds prevail. Additionally, third-generation wind power integrates sophisticated control systems and data analytics, enabling real-time monitoring and optimization of turbine performance. Machine learning algorithms help predict wind patterns and optimize blade angles for maximum energy efficiency. As these innovations continue to evolve, third-generation wind power holds the potential to drive down costs, increase the competitiveness of wind energy, and accelerate the global transition towards a sustainable and low-carbon future.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
19. Wind Turbines Impacts: Wind turbines have both positive and negative impacts on the environment and communities. On the positive side, wind turbines contribute significantly to mitigating climate change by generating clean, renewable electricity, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and lessening dependence on fossil fuels. They play a crucial role in transitioning towards a more sustainable energy mix. However, wind turbines can have some negative impacts as well. Their construction may lead to habitat disruption, affecting wildlife and bird populations, particularly if not carefully planned and sited. Noise and visual impacts can also be a concern for nearby residents, although modern turbine designs and appropriate siting help mitigate these effects. Additionally, wind turbines may pose risks to avian species, with the rotating blades posing a potential collision hazard. Proper environmental impact assessments and considerations during planning can help minimize these risks. Balancing the benefits and impacts of wind turbines is essential to ensure that wind energy continues to be a vital tool in combating climate change while addressing local concerns and environmental considerations.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
20. Hydro Power Technology: Hydropower technology harnesses the energy of flowing or falling water to generate electricity. It is one of the oldest and most widely used forms of renewable energy, providing a reliable and sustainable power source. There are two main types of hydropower systems: conventional hydropower and pumped-storage hydropower. Conventional hydropower involves the construction of dams across rivers to create reservoirs, which store water at higher elevations. The water is then released through turbines, producing mechanical energy that drives generators to generate electricity. This technology is highly efficient and capable of producing large amounts of electricity. Pumped-storage hydropower works as a form of energy storage. During periods of low electricity demand, excess electricity is used to pump water from a lower reservoir to a higher one. When demand increases, the stored water is released, flowing back down through turbines to generate electricity. Hydropower offers numerous advantages, including its ability to provide a stable and dispatchable power source, which complements intermittent renewables like solar and wind. It is also a clean energy source, producing minimal greenhouse gas emissions. However, the environmental impacts of hydropower can be a concern. The construction of large dams can lead to habitat disruption, altered water flow, and potential harm to aquatic ecosystems. Proper environmental assessments and sustainable planning are essential to mitigate these effects. Despite challenges, hydropower remains a critical component of the global energy mix, providing renewable and reliable electricity to millions of people worldwide. Continued research and innovation in hydropower technology will further enhance its efficiency and environmental compatibility, ensuring its contribution to a sustainable energy future.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
20.The Future of Renewable Energy: Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, geothermal, and hydroelectric power are rapidly becoming cost competitive with traditional electricity sources such as coal and natural gas. Additionally, the environmental and health advantages of renewable energy make it an appealing alternative for many individuals. Renewable objects, such as solar panels and wind turbines, will see more use as technology progresses and costs fall. Countries such as India, for example, have lately made significant investments in solar energy projects to assist satisfy their expanding energy demands while lowering carbon emissions. In addition to this type of governmental investment in renewable energy, private firms are investing extensively in R&D to reduce the cost of renewable technology even more so that they can compete.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
21.Power Generation: Electricity generation is defined as electricity generated from fossil fuels, nuclear power plants, hydro power plants (excluding pumped storage), geothermal systems, solar panels, biofuels, wind, etc. It includes electricity produced in electricity-only plants and in combined heat and power plants. Both main activity producer and auto producer plants are included, where data are available. Main activity producers generate electricity for sale to third parties as their primary activity. Auto producers generate electricity wholly or partly for their own use as an activity supporting their primary activity. Both types of plants may be privately or publicly owned. This indicator is measured in gigawatt hours and in percentage of total energy generation. There is a lot of power being made in power plants and power generators. We said that a spinning motion is transmitted to an alternator and the alternator transforms the motion into electricity. How does that happen exactly? An alternator is very much like an electric motor. Electric motors use electricity to spin a rotor. In alternators, it’s the reverse— instead of using electricity to create motion, alternators use motion to create electricity. In fact, many motors can function as makeshift alternators. Alternators are made up of two parts: a stator and a rotor. The rotor spins inside the alternator and is designed to create a magnetic field. The stator is essentially a box made up of many copper windings wrapped around a hollow iron core. When the rotor spins inside the stator, its magnetic field rotates too, and that rotation create an electrical current inside the stator’s windings. That electrical current is collected and sent to the power grid.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
22.Sustainable Development: Sustainable development is a concept that refers to meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It is a way of achieving economic growth, social development, and environmental protection in a balanced and integrated manner. Sustainable development involves three main components: economic, social, and environmental sustainability. These components are interconnected and must be considered together in order to achieve sustainable development. Economic sustainability involves ensuring that economic growth is achieved in a way that is socially equitable and environmentally sustainable. This requires promoting economic development that is inclusive, reduces poverty and inequality, and promotes social and economic justice. Social sustainability involves ensuring that social development is achieved in a way that is environmentally sustainable and economically viable. This requires promoting social welfare, reducing inequality, and improving access to education, healthcare, and other basic services. Environmental sustainability involves ensuring that natural resources and ecosystems are used in a way that is sustainable and does not harm the environment or compromise the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This requires reducing greenhouse gas emissions, protecting biodiversity, conserving natural resources, and promoting sustainable land use and urban planning. Sustainable development is a global challenge that requires collaboration and cooperation across different sectors and countries. It is essential for achieving a world that is prosperous, equitable, and environmentally sustainable for current and future generations.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
23.Waste-To-Energy: Waste-to-energy (WtE) is a process that involves the conversion of waste into energy in the form of electricity, heat, or fuel. The process typically involves the combustion of waste materials in specially designed power plants to generate energy. Waste-to-energy technology can be used to generate energy from a wide range of waste materials, including municipal solid waste (MSW), agricultural waste, industrial waste, and sewage sludge. The process can help to reduce the amount of waste that goes to landfill, and also provide a source of renewable energy. There are several different technologies that can be used for waste-to-energy, including incineration, gasification, and pyrolysis. Incineration involves the burning of waste at high temperatures to generate heat, which is used to produce steam and generate electricity. Gasification and pyrolysis involve the use of high temperatures and low oxygen environments to break down waste into a gas or oil that can be used to generate energy.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.
24.Green Energy and Economy: Renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, geothermal, and biomass are examples of green energy. It offers a great alternative to traditional energy sources such as coal, oil and natural gas. Green energy has been acknowledged as a critical component of any country's economy. It has the potential to create jobs in renewable energy businesses, boost economic growth through new business possibilities, and reduce emissions from the use of fossil fuels. Green energy may also help consumers save money on power while still delivering dependable service. Green economies are ones that employ efficient resource management strategies and foster long-term development with an emphasis on environmental conservation and social equality. This includes using renewable resources for production, promoting cleaner modes of transportation, employing cleaner manufacturing technology, increasing access to green products and services, creating jobs in the green economy sector, encouraging investment in the green economy sector, improving access to financing for small-scale businesses focused on sustainability initiatives, and engaging consumer demand for more sustainable products and services through education.
Related Associations: German Wind Energy Association | German Wind Energy Association |German Offshore Wind Energy Foundation| Wind Energy Network Bremerhaven |Wind Energy Agency| Lower Saxony Wind Energy Association | Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers Association |Wind Independent Power Producers Association |Indian Wind Energy Association |Tamil Nadu Spinning Mills Association |Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Developers Association
Related Journals: Wind Energy Science (WES) | Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics| Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic| Renewable Energy| Energy| Renewable Energy| Solar Energy Engineering | Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Related Conferences: Wind Energy Conferences| Solar Energy Conferences| Wind Turbines Conferences| Wind fibre Conferences| Thermal Energy Conferences| Off-shore Wind energy conferences| Renewable Energy Conferences| Power generation conferences| Power generation conferences.








